Unravelling the Mysteries of 2D Echocardiography: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction to 2D Echocardiography
In the landscape of modern medicine, diagnostic tools have sparked a revolution in understanding and treating cardiovascular diseases. Echocardiography, a non-invasive imaging technique, emerges as a pivotal instrument offering profound insights into heart structure and function. Among its modalities, 2D echocardiography emerges as a linchpin in cardiology, providing clinicians with intricate views of cardiac anatomy and physiology. This comprehensive guide navigates through the evolution, fundamentals, clinical applications, and future prospects of 2D echocardiography. Its significance lies in unravelling the complexities of heart conditions, guiding treatment strategies, and enhancing patient care. As technology advances, the potential for further innovations in echocardiography promises even greater precision and efficacy in diagnosing and managing cardiovascular disorders, thus reaffirming its indispensable status in modern cardiac care.
The Evolution of Echocardiography
The history of echocardiography dates back to the mid-20th century, marked by pioneering experiments employing ultrasound technology for heart visualisation. Since then, continuous innovation in imaging equipment and methodologies has elevated echocardiography into an indispensable diagnostic instrument. Beginning with rudimentary M-mode imaging, the field rapidly evolved towards more sophisticated techniques such as 2D echocardiography and beyond. These advancements have revolutionised cardiac imaging, empowering clinicians with real-time, high-resolution views of cardiac structures. Through decades of progress, echocardiography has transitioned from a nascent technique to a cornerstone of cardiovascular medicine, facilitating accurate diagnosis and management of a wide array of cardiac conditions with unprecedented precision and efficiency.
Understanding the Basics
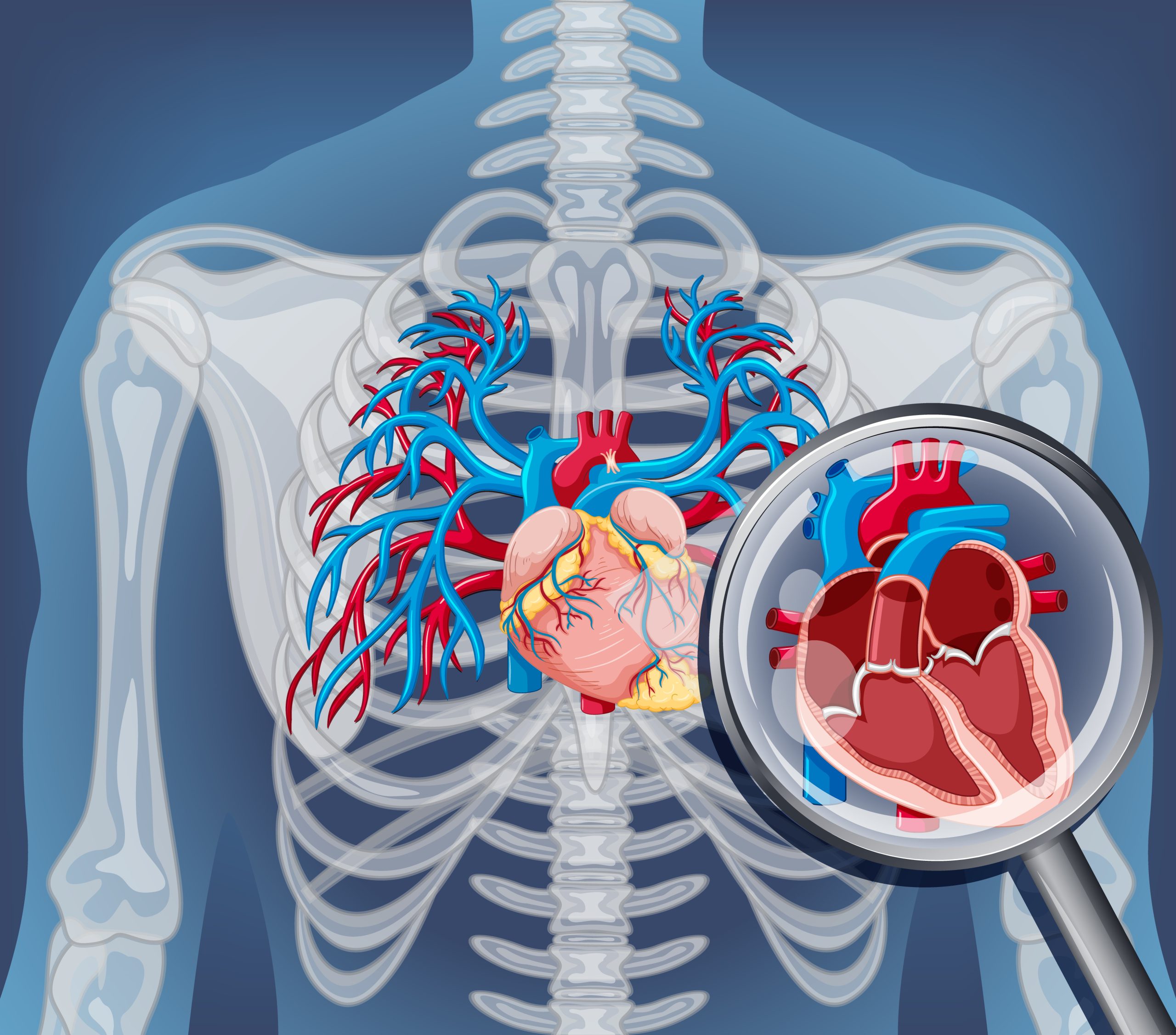
At its essence, 2D echocardiography harnesses the power of ultrasound waves to produce detailed, two-dimensional depictions of the heart. Using sophisticated technology, it emits high-frequency sound waves that penetrate the chest and bounce off cardiac structures. These reflections are then captured by ultrasound machines, translating into intricate images showcasing the heart’s chambers, valves, and the dynamics of blood flow. These visualisations serve as invaluable tools for clinicians, offering crucial insights into cardiac performance and facilitating the identification and treatment of diverse cardiovascular ailments. By providing real-time assessments of heart function, 2D echocardiography enables healthcare professionals to make informed decisions regarding patient care, enhancing diagnostic accuracy and optimising therapeutic interventions to improve cardiovascular health outcomes.
Pre-Echocardiogram Preparation
Before undergoing a 2D echocardiogram, patients are usually required to follow specific preparation guidelines to ensure optimal results. This typically involves fasting for several hours beforehand to reduce the presence of air in the digestive tract, which could interfere with the ultrasound imaging. Additionally, patients may need to refrain from taking certain medications, particularly those that affect heart rate or contractility, as they can impact the accuracy of the test. Wearing comfortable clothing is advised to facilitate easy access to the chest area for the ultrasound probe. Moreover, removing any jewellery or accessories is important to prevent obstruction and ensure clear imaging. Following these preparation guidelines helps healthcare providers obtain accurate and reliable echocardiographic results, aiding in the diagnosis and management of various cardiac conditions.
During the Procedure
During a 2D echocardiogram, patients recline on an examination table as a skilled technician or cardiologist administers a gel to their chest area. Using an ultrasound probe, called a transducer, the specialist manoeuvres it to capture detailed images of the heart. This non-invasive procedure is devoid of discomfort and is typically well-received by patients. By employing this method, healthcare providers gain immediate, real-time insights into both the anatomical structure and functional performance of the heart. The procedure aids in diagnosing various cardiac conditions, ranging from valve abnormalities to ventricular function assessment. Its painless nature and ability to offer instantaneous visual data make it a valuable tool in cardiology, facilitating prompt and accurate evaluation of heart health.
Clinical Applications and Benefits
2D echocardiography plays a pivotal role in the diagnosis and management of various cardiac conditions, including but not limited to:
– Assessing heart valve function and detecting abnormalities such as stenosis or regurgitation
– Evaluating cardiac chamber dimensions and wall motion abnormalities
– Detecting structural anomalies such as congenital heart defects
– Monitoring the progression of heart disease and assessing treatment efficacy
– Guiding interventional procedures such as cardiac catheterization and valve repair surgeries
The benefits of 2D echocardiography extend beyond diagnosis, offering clinicians valuable insights into disease progression and treatment outcomes.
Advanced Techniques and Technologies
In addition to standard 2D imaging, advancements in echocardiography have led to the development of various advanced techniques and technologies. These include:
– Doppler echocardiography for assessing blood flow velocity and direction
– Contrast-enhanced echocardiography for improving image quality and delineating cardiac structures
– Three-dimensional echocardiography for obtaining detailed volumetric reconstructions of the heart
– Strain imaging for quantifying myocardial deformation and assessing cardiac function with greater sensitivity
These advanced techniques enhance the diagnostic capabilities of echocardiography and contribute to more accurate disease assessment.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its many advantages, 2D echocardiography has certain limitations and challenges. These include:
– Limited acoustic windows in some patients, which may hinder optimal imaging quality
– Difficulty in visualising certain cardiac structures, particularly in individuals with obesity or lung disease
– Operator dependence, as obtaining high-quality images requires skill and expertise
– Inability to assess tissue characteristics such as fibrosis or inflammation, which may necessitate additional imaging modalities
Addressing these challenges requires ongoing research and innovation in echocardiographic technology.
The Future of 2D Echocardiography
In the foreseeable future, 2D echocardiography holds significant promise, buoyed by ongoing strides in imaging technology and data analysis methodologies. The advent of artificial intelligence-driven algorithms for image processing stands out as a beacon of progress, offering heightened diagnostic precision and streamlined workflows. Additionally, the development of miniaturised ultrasound devices heralds a new era of accessibility and portability in cardiac imaging, potentially revolutionising point-of-care diagnostics. Furthermore, the synergy between 2D echocardiography and complementary imaging modalities like cardiac MRI and CT holds immense potential for comprehensive cardiac assessment, facilitating a deeper understanding of both anatomical structures and functional dynamics. Through these convergences, the future landscape of cardiac imaging appears poised to deliver unparalleled diagnostic capabilities, paving the way for more informed clinical decision-making and ultimately, improved patient outcomes.
Patient Perspective
For patients undergoing 2D echocardiography, the experience typically involves minimal invasiveness and straightforwardness. Though mild discomfort may arise from the application of gel and pressure from the ultrasound probe, it is generally well-tolerated. The procedure’s non-invasive nature ensures that most individuals can undergo it without significant distress. Furthermore, the diagnostic insights gleaned from echocardiography are invaluable, aiding patients in understanding their cardiovascular health and available treatment choices. Armed with this information, individuals can make informed decisions about managing their cardiac well-being, potentially leading to earlier interventions and improved health outcomes. Thus, while the procedure may involve temporary discomfort, its benefits in terms of diagnosis and patient empowerment outweigh any momentary inconveniences.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Is echocardiography safe? Yes, echocardiography is considered safe and non-invasive, with no known risks or side effects associated with the procedure.
- How long does a 2D echocardiogram take? The duration of a 2D echocardiogram typically ranges from 30 to 60 minutes, depending on the complexity of the examination.
- Are there any risks associated with the ultrasound gel used during the procedure? The ultrasound gel used during echocardiography is hypoallergenic and generally safe for use on the skin.
Conclusion
In conclusion, 2D echocardiography serves as an indispensable cornerstone in cardiovascular imaging, providing clinicians with a vital window into the complex mechanisms of the heart. From its modest origins to the state-of-the-art technology available today, echocardiography has continuously advanced, propelling innovations in cardiac diagnosis and patient management. By unveiling the intricacies of cardiac anatomy and function, 2D echocardiography remains an invaluable asset in the battle against cardiovascular disease, significantly enhancing patient outcomes and quality of life on a global scale. Its ability to offer real-time insights and non-invasive assessments underscores its pivotal role in guiding therapeutic decisions and monitoring treatment efficacy. As technology progresses, the future promises even more refined techniques, reaffirming echocardiography’s status as a fundamental tool in cardiovascular care, continually striving for enhanced precision and patient-centric outcomes.
![]()